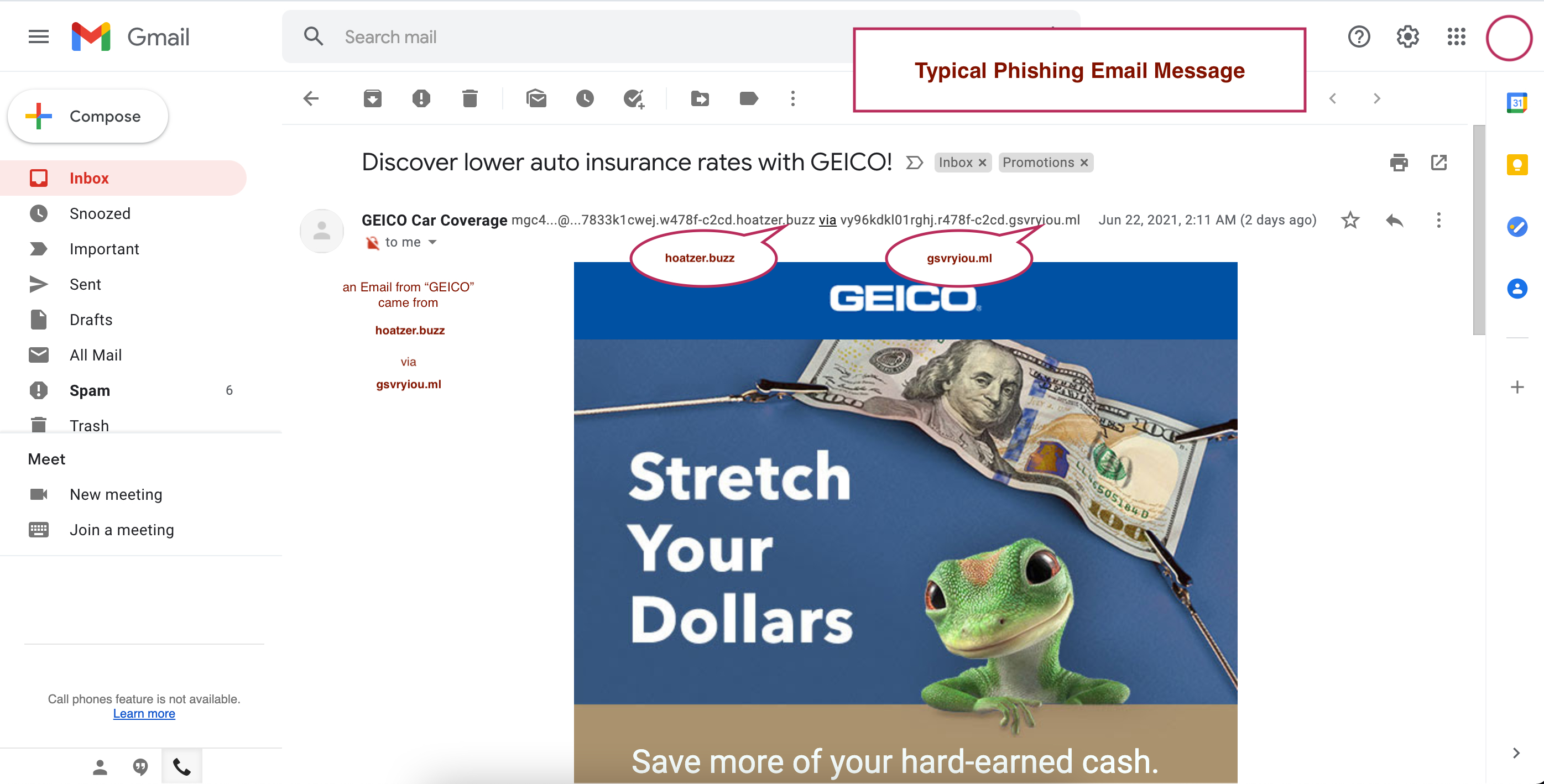
Phishing uses a deceptive art. This is when someone sends emails that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as an order notice or a bank deposit, but are actually from someone who is trying to collect sensitive information from you, stuff such as passwords, bank account information or medical records. In most cases these are mass email blasts, aimed at a wide variety of individuals and hoping that a few will "bite" (click).
The ultimate goal for most phishing emails is to collect information such as bank accounts, usernames / passwords and even medical or identity information. For some of this information, it is easy to see how a hacker could use the information, such as a bank account. Unfortunately, other information can be just as valuable when sold on the dark web: things like social security numbers, medical records, and passwords to various services or eCommerce accounts like Netflix or Spotify, Amazon, Google, etc.
Do's and dont's to protect from phishing
- Don't click on links, try to mouse over to see where the link goes, but don't click.
- Do examine email header.
- Do check the grammar.
- Do look for unusual wording.
- Do look for "out of the blue" requests like "pay this bill" from you CFO.
- Do call and verify any requests if an email comes from your colleague or client, vendor.